1. Introduction
The digital revolution has transformed the accounting profession and its practices (Pratama, 2024), including management accounting (MA) roles and routines. This transformation has also impacted the responsibilities of management accountants, which have evolved from reporting aggregated historical values to including performance measurement and providing management with relevant information for decision-making (Appelbaum et al., 2017). These advances result from several factors, including technological innovations, business needs, regulatory changes, and shifts in work practices due to digitalisation (Rautiainen et al., 2024; Tiitola et al., 2024).
In line with this change, scientific research on the intersection between MA and digital technologies has significantly increased in recent years. This increase is motivated by the desire to understand how integrating technological innovations in MA routines may enhance strategic decision-making and business sustainability. In addition, these discussions are driven by the demand for real-time information, changes in regulatory and accounting standards, the need for efficiency and cost control, and growing interest in sustainability and social responsibility issues. In this context, these academic discussions have been addressed through a multidisciplinary approach under different technological perspectives, including big data, digitisation and transformation of accounting information, business intelligence and analytics (BI&A), management control systems (MCS), artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning (ML), and blockchain.
Research has shown that innovations in MA offer various benefits such as improved efficiency, productivity, security (Faccia & Petratos, 2021), and time and cost reductions (Poyda-Nosyk et al., 2023). However, there are challenges related to a lack of digital competencies, including statistical and econometric skills (Nielsen, 2018; Steens et al., 2024), which are considered barriers to the acceptance and adoption of digital technology by management accountants. These challenges hinder their ability to fully leverage the benefits that these technologies can provide. These competencies are essential for these professionals to take advantage of technological opportunities in the strategic decision-making process (Vărzaru, 2022c), considering the expanded digitalisation has intensely increased the type and amount of data available, generating a growing need for new ways to create value using them (Ranta et al., 2023).
Despite the challenges, many organisations are integrating BI&A techniques into MA tasks to improve data collection, analysis, and information delivery, supporting decision-making (Rikhardsson & Yigitbasioglu, 2018). Moreover, the rise of AI, especially ML, has significantly impacted industry, leading to better customer service, improved operating performance, and increased revenue (Ranta et al., 2023). These applications of AI must be expanded to adapt to the highly competitive, uncertain, and dynamic context in which organisations operate. Thus, it has become increasingly necessary to develop new organisational forms, structures, decision-making methods, and processes that promote continuous learning and adjust the organisation to its environment.
In this sense, the purpose of this study is to contribute to academic discussions through a systematic literature review that combines bibliometric analysis and science mapping techniques applied to a bibliographic sample of 140 articles extracted from Scopus and Web of Science (WoS). The specific objectives are to analyse this bibliographic sample applying bibliometric performance analysis and science mapping techniques to provide an overview of the current state of this knowledge field, map its conceptual structure, understand the evolution of academic debates, identify gaps, and provide insights for future research.
Although recent literature reviews applying bibliometric analysis or science mapping techniques involving aspects of MA and digital technologies have been published, the bibliometric articles identified – which are also part of this sample – addressed specific issues related to MA and digital technologies, such as small and medium-sized enterprises’ (SMEs) default prediction using AI to improve predictive models (Ciampi et al., 2021), the use of big data in accounting (Aboagye-Otchere et al., 2021), big data processing in cloud-based accounting information system (AIS) (Ionescu, 2022), blockchain technologies in supply chains (Sahoo et al., 2022), blockchain in accounting (Shkulipa, 2021), and the use of Twitter (now X)[1] in MA research (Kurnianingrum et al., 2023).
This study explores the intersection of MA and digital technologies from multiple perspectives, without concentrating on any specific technology to thoroughly examine and understand the most relevant technological trends within MA research. Moreover, considering the complexity and interdisciplinary discussions on MA and digital technologies, multiple methods’ approaches were applied to systematically explore and understand the state of the art in this knowledge field.
This multidisciplinary perspective is relevant because, in an evolving environment where digital technologies have impacted MA roles and practices, it is important to reflect on whether MA research is following this evolution. According to Ranta et al. (2023), there is limited knowledge about these changes and their impact on MA research, including potential research agendas, new data, methods, and theoretical development. Thus, it is relevant because digitalisation is increasingly influencing research in MA due to a wide array of data, which creates new opportunities for both qualitative and quantitative research (Bhimani, 2020), new concepts, variables, and mechanisms that reinforce the relevance of research for corporate practice (Mahlendorf et al., 2023).
Considering the relevance and urgency of these discussions, this study contributes to providing useful insights for researchers, academic accountants, management accountants, professional accountant organisations, and policymakers. First, this research enriches scientific debates by analysing the state of the art, identifying trends and research opportunities, and examining how MA research is changing due to technological advancements. Furthermore, this study contributes to discussions about the relevance of universities in updating their accounting curricula to prepare future management accountants with the necessary skills for a digitally driven environment. It is a relevant discussion considering that the fast technological development requires accounting professionals to be highly competent in utilising software and accounting tools (Oleiwi, 2023), including data analytics skills and knowledge of data science tools (Koh et al., 2023). In this sense, it is necessary to adapt accounting programs and pedagogical models, including practical training using new teaching methods based on experiential learning (Sidorova et al., 2023) and rigorous data analytics training into universities’ existing curriculum (Koh et al., 2023).
For managers and accountants, this study helps to expand their understanding of how MA practices and tools have been transformed due to technological advances. In addition, it helps them understand the importance and urgency of increasing their levels of knowledge and analytical skills (Steens et al., 2024), improve competency analysis from a descriptive perspective to provide predictive and prescriptive informed decision-making (Appelbaum et al., 2017), enhancing their career opportunities, and adding value in the decision-making process.
Accounting professional organisations also benefit from this study in developing their strategies and policies, especially regarding advanced digital competencies issues. Although professional accounting bodies address this need by emphasising continuing professional education and developing guidelines for data analytics (Koh et al., 2023), advanced digital competencies have only recently been added to the top-line skills in the competency frameworks defined by most accountants’ and controllers’ professional bodies (Steens et al., 2024). Furthermore, this study provides insights to government and policymakers through recent research discussions related to MA and digital technologies. These insights may be helpful in inspiring policy-making strategies to foster economic growth. Some strategies may be related, for example, to improving workforce skills, promoting research and development (R&D), and environmental sustainability efforts (Rothstein, 2024).
This study is structured as follows. First, the background section emphasises key conceptual aspects. Then, the methods section is presented, followed by the results and analysis, and finally, the conclusion.
2. Background
2.1 The Role of Management Accounting
MA is a process for providing managers with relevant financial and non-financial information (Appelbaum et al., 2017; Mauludina et al., 2023). It is commonly referred to as a decision-supporting activity (Rikhardsson & Yigitbasioglu, 2018) because it uses information from accounting records to support managers’ decision-making (Warren et al., 2015). However, considering the increasing availability of data generated by technological innovations, the role of MA has been transformed over the years, evolving from focusing primarily on budgetary control and costing to developing and implementing strategies that foster increased firm performance (Richins et al., 2017).
In this sense, the functions of MA have been increasingly expanded, and the role of the management accountant has been required to assist managers in performing their duties by developing systems that align organisational goals (Warren et al., 2015), formulating and implementing strategies, monitoring their achievement, and advising on and executing corrective actions as necessary (Richins et al., 2017). In addition, considering a business world that requires more timely information and the increasingly decentralized MA functions (Rikhardsson & Yigitbasioglu, 2018), its traditional focus has been extended. It now includes identifying internal and external drivers of financial performance, leading the management accountant to become a business advisor who takes proactive steps to aid executives and decision-makers (Appelbaum et al., 2017).
This transformation brings opportunities and challenges for management accountants. Opportunities include developing expertise in strategy formulation and implementation, monitoring the attainment of the firm’s strategic objectives (Richins et al., 2017). On the other hand, one of the greatest challenges is correctly handling immense volumes of data. All organisations need data and advanced analytics to improve their business decisions (Nielsen, 2022). However, to increase the power of analysis, management accountants must develop the capability to identify and interpret relevant data that can be turned into implementable strategies (Richins et al., 2017). The increasing availability of data in the modern world has brought discussions, concepts, and solutions regarding processes and technologies for analysing it, such as big data, big data analysis, big data systems, and business intelligence.
2.2. Main Technology-related Terms within MA Studies
Big data refers to voluminous datasets of structured or unstructured data that cannot be reasonably analysed using database management systems or traditional software programs (Warren et al., 2015). Big data analytics is the process of analysing large volumes of structured and unstructured data (Richins et al., 2017) to identify patterns, trends, and insights for improving business decision-making (Franke & Hiebl, 2023). It can facilitate the discovery of essential measures to be incorporated into management control systems, contributing to tracking and improving productivity (Warren et al., 2015). Big data technologies refer to tools used to process and analyse large volumes of data that cannot be processed through conventional systems due to the volume and variety of data (Bhimani & Willcocks, 2014). Employing big data technologies, aggregate data can be analysed through data mining to identify outliers and other irregularities, assisting auditors, management, and other stakeholders (Warren et al., 2015).
Business analytics examines big data to discover patterns with a broader focus on statistical analysis and predictive modelling (Appelbaum et al., 2017) focusing on developing new insights and understanding to improve business performance (Nielsen, 2023). Business intelligence refers to capabilities that enable organisations to make better decisions (Appelbaum et al., 2017). This term is used to describe an ecosystem of tools that can transform raw data into actionable insights that help make better strategic, tactical, and operational decisions (Igulu et al., 2023), seeking to reduce costs, increase productivity, and enhance profitability of the organisation (Bao et al., 2023), and help managers and other stakeholders understand business and market information (Järvenpää et al., 2023).
In addition, AI-based technologies are applied to perform efficient and effective analysis. Other uses of AI applications, such as generative artificial intelligence (Dogru et al., 2023) and machine learning algorithms (Nielsen, 2022) are also being explored to support decision-making in MA. According to Dogru et al. (2023), generative artificial intelligence has the potential for value co-creation in the accounting and finance discipline in several ways. For instance, it can offer improved and contextual responses in conversational finance, which can provide precise answers to users’ financial questions (Dogru et al., 2023). ML enables computers to perform tasks without human involvement by detecting patterns and learning to make predictions and recommendations through data processing and experiences rather than by following explicit programming instructions (Nielsen, 2022). Although AI and related technologies create potential business value (Elbashir et al., 2011), their adoption provides an opportunity for management accountants proficient at analysing and obtaining insights from data (C. Zhang et al., 2023).
Another emerging technology impacting MA is blockchain. This distributed ledger technology offers a secure and transparent way to perform and record transactions in a sequential and immutable manner (Kostić & Sedej, 2022). It allows users to transfer money, stocks, bonds, or other important assets in a secure, private, and more cost-effective way (Shkulipa, 2021). Blockchain has applications in various areas, including accounting, auditing, and MA. As Al-Zaqeba et al. (2022) explain, this technology has multiple uses in various fields, especially in accounting and in the processing and exchange of financial data in a safe, reliable, and transparent manner that enables easy access. The possibility of programming audit rules onto blockchain and real-time reconciliation facilitate the auditing processes of accounting records for financial reporting (Kostić & Sedej, 2022).
In the MA field, blockchain technology can potentially improve management accounting systems, leading to better resource utilisation and cost reduction and contributing to sustainable accounting practices (Nguyen et al., 2023). In addition, according to Kostić and Sedej (2022), blockchain can help to improve MA practices in facilitating decision-making and allowing more accurate information, considering its transparency and immutable ledger, real-time data access, improved control mechanisms, and cost reduction. Recent studies have shown some uses of blockchain in MA, including information exchange among organisations, enabling independent firms to collaborate without relying on a single controlling entity (Kostić & Sedej, 2022). Moreover, blockchain can enhance data security and privacy in cloud computing using Ethereum smart contract (Albaroodi & Anbar, 2022). Furthermore, integrating blockchain into enterprise asset management accounting system can improve efficiency and accountability by combining cost control with a responsible asset management approach (Wang et al., 2024).
Despite the benefits, blockchain technology still faces challenges and barriers to its applicability in the context of accounting and MA, for example technical complexity, cost of implementation, systems integration issues, cultural resistance, and regulatory and compliance concerns (Kostić & Sedej, 2022; Nguyen et al., 2023). In addition, although blockchain offers transparency, it can also raise privacy issues related to sensitivity, considering financial information may be exposed on a public ledger, which could conflict with regulations that protect personal information (Albaroodi & Anbar, 2022; Wang et al., 2024). Furthermore, the lack of standardisation in blockchain protocols, the lack of specialised knowledge and skills (Wang et al., 2024), and infrastructure limitations, especially in the context of developing countries (Nguyen et al., 2023) were considered barriers to blockchain implementation in MA contexts.
Further to the technologies discussed above, studies in MA that involve digital technologies have also addressed other specific technological terms related to this field, such as cloud computing (Al Lami et al., 2019; Qin & Qin, 2021), information systems quality (Papiorek & Hiebl, 2023), enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems (Faccia & Petratos, 2021), and robotic process automation (RPA) (Korhonen et al., 2021; Rautiainen et al., 2024).
2.3. Advances in Digital Technologies and the Nature of Management Accounting
Advances in digital technologies have raised debates about the nature of MA. The main reason is the transformation that MA has experienced moving from traditional, retrospective reporting to a more dynamic and strategic role within organisations (Appelbaum et al., 2017). Considering these transformations, reflecting on the nature of MA is crucial for further advancements and necessitates continuous learning. According to Bhimani and Willcocks (2014), in addition to technological advances affecting new organisational forms, the ways businesses create and transform information are reshaping how they advance innovations in the creation of corporate value.
These innovations have enabled management accountants to access various data types, store them, and benefit through enhanced computing capabilities (Appelbaum et al., 2017), requiring them to develop a more business-oriented and strategic role (Rikhardsson & Yigitbasioglu, 2018). However, according to Appelbaum et al. (2017), the nature and scope of MA has barely changed, and management accountants employ mostly descriptive analytics, some predictive analytics, and a minimum of prescriptive analytics. Instead, they should augment their roles, considering that technology currently makes it possible. As Appelbaum et al. (2017) explain, it enables them to utilize data analytics techniques to answer questions related to three key areas: descriptive analytics (what has happened), predictive analytics (what will happen), and prescriptive analytics (what is the optimized solution).
In line with this, Nielsen (2018) argues that management accountants should adopt a holistic approach within an analytics culture. This involves collaborating with other operational areas to identify their impacts. In such a culture, decision-making norms, behaviours, values, and outcomes should align to ensure that analytical insights create real value rather than just promising potential benefits. Nielsen (2018) also emphasised the implications for management accountants in this analytics movement: concentrating on information-based decisions that generate value, making predictions and forecasts, enhancing the visualisation of the reporting process, and developing the necessary skills for business analytics. However, considering the highly technical nature of exploratory analyses, data scientists have a comparative advantage and should take a lead role in exploratory analysis (Richins et al., 2017).
Additionally, the literature reflects on whether MA should maintain the same methodologies and methods in a constantly evolving technological environment (Bhimani, 2020). An important challenge is how MA can improve its methods to take advantage of technological advances (Appelbaum et al., 2017). The consensus is that big data is a disruptive force in accounting, considering the data recording task has increasingly become less important, making some MA techniques obsolete, changing the role of accounting in decision-making processes and requiring significant changes in the skill sets of management accountants (Rikhardsson & Yigitbasioglu, 2018). Considering this evolution, a re-evaluation of established methods and methodologies to address growing and ongoing transformations is required, and the role of management accountants should change significantly, positioning them as business advisors who proactively support executives and decision makers (Appelbaum et al., 2017). In this context, Rikhardsson and Yigitbasioglu (2018) highlighted the need to develop research to study the changing roles of management accountants and the decentralization of the MA function provided by digital technologies. Moreover, it is essential to use various theoretical perspectives to fully understand the changes brought about by big data and digitalisation and their impact on the MA field (Rikhardsson & Yigitbasioglu, 2018).
3. Method
This study adopted multiple methods, namely systematic literature review protocols, bibliometric performance analysis, and science mapping techniques, to comprehensively explore research on MA and digital technologies retrieved from the Scopus[2] and the WoS[3] databases. Due to the exponential growth of research and the time requirements for assessing and evaluating new information, it is difficult to stay up to date with new developments (Linnenluecke et al., 2020). Therefore, it is increasingly necessary to enhance the level of rigor when conducting a literature review. This is proposed because knowledge production within business research is accelerating rapidly while remaining fragmented and interdisciplinary (Snyder, 2019). In this context, the multidisciplinary nature of business and management studies raises the complexity of writing a critical review as it requires scholars to carefully define which theories, subject areas, and texts are most appropriate to examine considering the study’s focus and objectives (Mitchell & Rich, 2022).
Conducting literature reviews systematically can ensure the quality, replicability, reliability, and validity of these reviews (Page et al., 2021; Xiao & Watson, 2019). In recent years, increasing attention has been dedicated to the systematic study of literature, due to the availability of online databases and the development of tools capable of conducting automatic analyses (Aria et al., 2020). Indeed, several innovations in conducting systematic reviews have emerged, including novel methods (Pagani et al., 2023) and technological advancements to identify relevant evidence (Page et al., 2021). However, researchers in business, management, and related fields often depend on superficial and narrative reviews that do not systematically investigate developments in the literature (Linnenluecke et al., 2020).
Although systematic literature review and bibliometric analysis are different types of review methods with different purposes, as highlighted by Donthu et al. (2021), if combined, these methods may offer benefits to advance theory and practice (Mukherjee et al., 2022). According to Donthu et al. (2021), the application of bibliometric analysis in business research is relatively new, and in many instances, underdeveloped. Bibliometric analysis is a method for analysing large datasets to investigate their evolution and give insights on emerging areas (Donthu et al., 2021), based on statistical techniques (Aria et al., 2020). Bibliometric research encompasses two main types of analytical techniques: performance analysis and science mapping (Aria et al., 2020; Donthu et al., 2021; Mukherjee et al., 2022). The first refers to an evaluative technique used to assess productivity and impact, while the second describes a relational technique for identifying knowledge clusters within a field (Mukherjee et al., 2022). Thus, given the importance of integrated methods for ensuring a transparent, and replicable exploration of literature, this study employed multiple approaches.
3.1 Research Strategies
The research strategies applied in this study considered a longitudinal analysis of a scientific bibliographic sample, under quantitative and qualitative perspectives, including Methodi Ordinatio (Pagani et al., 2023), the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) statement (Page et al., 2021) and bibliometric performance analysis techniques and science mapping (Aria et al., 2020; Aria & Cuccurullo, 2017; Donthu et al., 2021; Mukherjee et al., 2022; N. J. van Eck & Waltman, 2009), to answer the two research questions. Research Question 1 (RQ1) asks:
What is the current state of management accounting research on digital technologies?
RQ1 aims to provide an overview of the scientific production, based on bibliometric performance analysis techniques. This analysis explores the main characteristics of the metadata sample, including the evolution of scientific production, authors, journals, and countries.
Research Question 2 (RQ2) asks:
What are the main characteristics of the conceptual structure of the bibliographic sample on management accounting and digital technologies?
RQ2 aims to explore the scientific production applying science mapping techniques through cluster analysis. Here the objective is performing relational analysis to understand the frontier knowledge on this topic applying term analysis to examine the existing relationships among topics discussed to identify trends, gaps and provide insight into future lines for research.
3.2 Sample Selection Process and Research Workflow
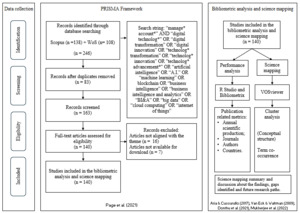
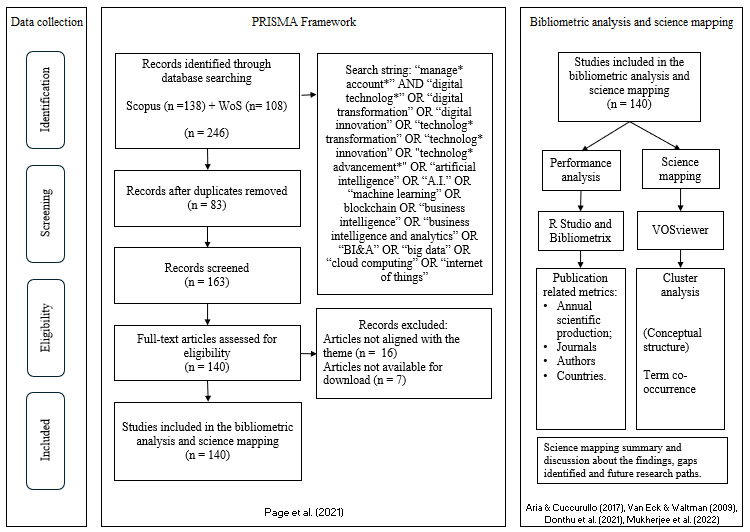
To address the research questions, this study systematically applied methods and techniques in multiple steps to ensure a comprehensive, transparent, and replicable process – Figure 1 illustrates the steps. The first phase considered an exploratory preliminary stage of the research to establish the foundation of the subject field and understand front-line knowledge to select the most appropriate keywords for the systematic literature review process, as highlighted by Rikhardsson and Yigitbasioglu (2018). The second phase includes the PRISMA method. This is a guideline designed to address reporting of systematic reviews (Page et al., 2021). In this stage, the same query string and similar filters’ parameters were applied in both databases: “Article” for document type, and “English” for language, resulting in a final sample of (140) articles retrieved from Scopus and WoS, published from 1992 to 2024. This timeframe includes all publication years from the dataset, excluding those filtered out during the screening and eligibility phases.
The next step was to export the metadata in the BibTex file format from both databases to merge them in the RStudio using the Bibliometrix package. In this process, 83 duplicated records were removed, resulting in a sample of 163 articles for analysis. The next step was to read all titles and abstracts to check if all articles were aligned to the theme. In this process, 16 articles were excluded considering they were not related to the scope of the research, and seven articles were not available for download, resulting in a final sample of 140 articles. Then, the bibliometric performance analysis and science mapping were performed. To execute the bibliometric performance analysis, the RStudio was used along with the Bibliometrix package to enable data visualization and analysis. The Bibliometrix is an open-source R-package for performing comprehensive bibliometric analyses – see Aria and Cuccurullo (2017). This package was applied to visualize information related to evolution of the research, most relevant authors, most relevant articles, journals, and countries. The cluster analysis was performed using the software VOSviewer, a free program for constructing and viewing bibliometric maps – see van Eck and Waltman (2010).
4. Results and Analysis
4.1 Bibliometric Performance Analysis (RQ1)
4.1.1 Annual Research Output
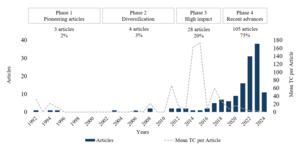
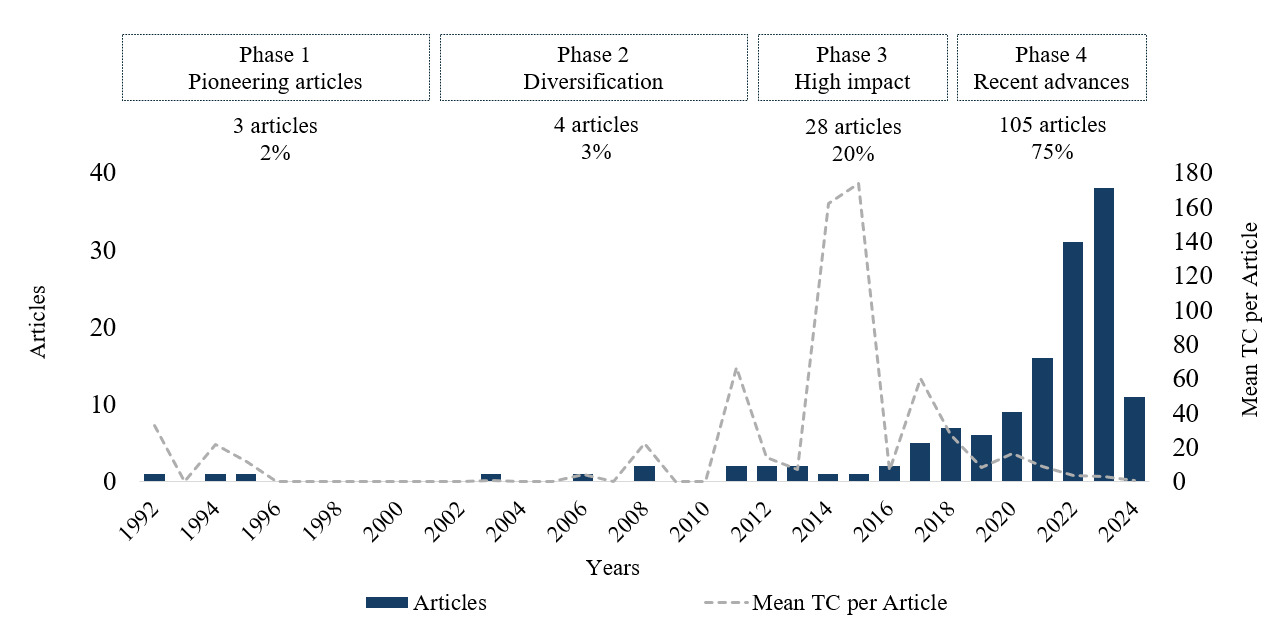
Over the last few decades, MA has made significant steps forward into new areas and dimensions, including various innovative techniques (Abdullah et al., 2022) and technological innovations. The accounting profession and its practices have transformed rapidly over time (Pratama, 2024), including the management accountant’s responsibilities, which have been evolving from just reporting aggregated historical value to also considering organisational performance measurement and supporting administration with decision-related information (Appelbaum et al., 2017). This is observed in this bibliometric analysis, which showed 75% of the articles analysed was published in the last five years. Figure 2 depicts the annual research output, along with the mean of total citations per article for this sample of 140 papers. It illustrates exponential growth in recent years. The highest absolute output occurred in 2023, with 38 articles published. However, the most significant annual growth rate was observed in 2022, with 31 articles published compared with 16 in 2021, an increase of approximately 94%. This growth in output in recent years can be explained due to technological advancements (Steens et al., 2024), the demand for real-time information (Appelbaum et al., 2017), regulatory changes and accounting standards’ (Nielsen, 2022) need for efficiency and cost control (Kuzey et al., 2019), and growing interest in sustainability and social responsibility (Di Vaio et al., 2023).
To analyse the evolution of the main study topics within this data set, the period under analysis was divided into four main phases, each representing the main common characteristics of the studies that comprise each period. Although there was little scientific development, Phase 1 (1992–2002) included pioneering articles, including three articles (c. 2% of the sample), followed by a period with no publications. This period of limited output can be attributed to the emerging stage of digital technology integration into MA. In this phase, one important article relates to incorporating AI in the accounting curriculum by Baldwin-Morgan (1995), as it can be considered a relevant, seminal, but up-to-date, debate. Although, with only four articles published (c. 3% of the sample), Phase 2 (2003–2010) marks the beginning of diversification and an expansion of themes. The articles that received the highest mean total citations during this phase focused on the diffusion of innovation theory (Askarany & Smith, 2008), and customer profitability (Gleaves et al., 2008).
Phase 3 (2011–2019) is characterized by the highest mean and total citation within the sample. In addition, this phase stands out for the increase in published articles, totalling 28 (c. 20% of the sample). The discussions during this phase are diverse and impactful, contributing significantly to academic debates. Key studies in this phase included Bhimani and Willcocks (2014) and Warren et al. (2015), which focused on the influence of big data on the transformation of accounting practices. Phase 4 (2020–2024) is characterized by contemporary debates that are beginning to register scientific impact. Additionally, the articles from this phase were published during and after the pandemic, at a time when the world was addressing global challenges. This phase includes 105 articles (c. 75% of the sample) and reflect ongoing discussions about the integration of digital technologies into MA. So far, some of the most influential articles during this period have addressed debates related, for example, to the impact of digitalisation in accounting and MA practices (Bhimani, 2020; Knudsen, 2020), the circular economy (Di Vaio et al., 2023), and SME risk reduction (Ciampi et al., 2021).
Phase 1 (1992–2002) – 3 Articles. As noted, three articles on MA and digital technologies were published between 1992 and 2002. In this period, the discussions focused on the impact of organisational culture on technological innovation (Demirag & Tylecote, 1992), how hierarchical organisation inhibits MA innovation (Foster & Ward, 1994), and the advantages of incorporating AI into the accounting curriculum (Baldwin-Morgan, 1995). These themes continue to be relevant and essential nearly three decades later. There is a need for reflection and paradigm shifts so that accounting and MA practices can evolve with technological advances and make the best use of technology to perform its functions more effectively. According to Munir et al. (2023), despite the relevance of organisational culture in organisational practices and decision-making processes, there is a lack of empirical research on how cultural factors impact the adoption of effective, innovative MA techniques and strategies.
Regarding incorporating AI into the accounting curriculum, Baldwin-Morgan (1995) argued that in an environment where the use of expert systems for accounting tasks is increasing, future accountants should learn about AI during their undergraduate studies. Considering that accounting knowledge evolves, universities and professionals must remain attentive to its development (Pratama, 2024). However, according to Franke and Hiebl (2023), educational programs for management accountants’ skills addressing the question of tacit MA knowledge in organisations may largely deviate from textbook-like learning, highlighting the necessary skill is adopted through practice and experience in an organisation.
Phase 2 (2003–2010) – 4 Articles. From 2003 to 2010, four articles were published on MA and digital technologies from different perspectives: economic conditions (Hussain, 2003), ethics within technological innovation (Vuokko, 2006), diffusion of innovation theory (Askarany & Smith, 2008), and customer profitability (Gleaves et al., 2008). Hussain (2003) examined how economic conditions affect MA performance measures in the banking sector. The study highlighted deficiencies in accounting-based performance measures and MA systems in uncertain economic and competitive environments, emphasizing the necessity for adaptability and responsiveness to technological advancements in such environments. Additionally, a context of social care, the study developed by Vuokko (2006) focused on work ethics, technology, care workers, and managerial accountability. It aimed to introduce mobile technology to upgrade services and improve managerial planning efficiency. The study recommended examining the ethical implications of technology in social work settings due to the potential unintended consequences of implementing mobile informatics technology, which can challenge the original project objectives and hinder organisational effectiveness.
Furthermore, based on the diffusion of innovation theory, Askarany and Smith (2008) explored the relationship between business size and the diffusion of technological innovation and activity-based costing (ABC) as an administrative innovation. They emphasized the lag in the diffusion of cost and MA changes compared with technological innovations. According to Askarany and Smith (2008), despite the high rates of manufacturing innovations, the diffusion of ABC was still much lower than those of traditional accounting systems, indicating that administrative innovations do not keep pace with technological changes in manufacturing practices, emphasizing the need for a strategic approach to facilitate the diffusion of these innovations effectively.
Lastly, the synergy between MA and marketing in the context of customer profitability was studied by Gleaves et al. (2008). Per their study, the gap between MA and marketing is diminishing due to advancements in MA measures, increased pressure on marketers to demonstrate their value, and technological progress in database management. Based on their findings, Gleaves et al. (2008) argued that there is a need for consistent definitions and methodologies related to the calculation of customer profitability, customer equity and customer lifetime value, including the treatment of customer acquisition costs, profit versus cash flow basis, and the inclusion of intangible customer values.
Phase 3 (2011–2019) – 28 Articles. During this period, studies addressed several discussions, perspectives, and approaches related to advancements in MA and digital technologies. These include debates on the impact of big data on accounting information (Warren et al., 2015) and MA practices (Richins et al., 2017), the integration of business analytics into MA systems (Appelbaum et al., 2017; Rikhardsson & Yigitbasioglu, 2018), cost system functionality (Kuzey et al., 2019), factors influencing target costing adoption (Rasit & Ismail, 2017), cryptocurrencies (Zadorozhnyi et al., 2018), cloud computing (Strohmeyer & Wenngren, 2011), cloud computing in the context of SME (Al Lami et al., 2019), and social technology integrated strategy and risk management (Lenk et al., 2019). Studies debated the impact of the big data revolution in accounting (Warren et al., 2015), accounting information and MA practices, highlighting their benefits and challenges (Bhimani & Willcocks, 2014). According to Warren et al. (2015), in addition to contributing to the development and evolution of MA systems and budgeting processes, big data can be viewed as a corporate asset useful for decision-making and improving business performance and profitability. Furthermore, the availability of big data is also bringing in a possible redesign of organizing executive responsibilities (Bhimani & Willcocks, 2014), requiring professionals to develop analytical skills and knowledge to effectively leverage this data (Appelbaum et al., 2017).
Studies focusing on the integration of business analytics in MA systems have emphasized its relevance in developing organisational capability and empowering operational levels (Elbashir et al., 2011). It acts as a strategic enabler for MCS (Marx et al., 2012), enhancing decision-making support (Rikhardsson & Yigitbasioglu, 2018), and incorporating predictive and prescriptive analysis to ensure high-quality performance management (Appelbaum et al., 2017). Discussions also addressed how information technology (IT) enhances cost system functionality by providing detailed, accurate, and timely data to support advanced managerial accounting practices and decision-making processes (Kuzey et al., 2019). A more recent development involves research on cryptocurrencies, which highlights the benefits of implementing blockchain technology for effective MA. These benefits include confidentiality, complete automation of accounting processes, data integration and accessibility, cost reduction, increased control, and transparency (Zadorozhnyi et al., 2018).
Phase 4 (2020–2024) – 105 Articles. In recent years, the number of articles published on MA and digital technologies has significantly increased. Around 75% of the papers in the sample emerged during this period. The growth was clear not only in quantity but also in new perspectives on the theme. Studies discussed specific digital technology-related terms, such as big data, BI&A, AI, ML, blockchain, and cloud computing, exploring these terms, concepts, and their applications from different perspectives. However, a common theme in most studies was integrating these technological advances into accounting systems, MA systems or MCS, for strategic decision-making aimed at sustainable business performance and generating value for MA professionals, businesses, and the environment.
Recent studies on “big data” highlighted several key perspectives regarding its impact on the evolving role of MA practices. Bhimani (2020) discussed the implications of digitalisation and big data, while Cavélius et al. (2020) and Tiron-Tudor and Deliu (2021) examined the disruptive effects on management accountants. Moreover, there is a growing emphasis on the need for professionals to develop new skills and abilities, particularly in strategic analysis of large data sets, to provide added value, involving sophisticated decision-making based on predictive and prescriptive analysis (Franke & Hiebl, 2023). In the context of the term “BI&A”, studies have investigated the success factors for implementing BI&A tools in MA practices and how these tools affect organisational and individual performance (Mauludina et al., 2023; Mudau et al., 2024). In addition, some studies have assessed BI&A tools concerning budgeting, costing, and performance evaluation (Kielanowicz et al., 2023; Youssef & Mahama, 2021), and organisational culture to evaluate the impact of big data analytics capabilities on organisational innovation performance (Munir et al., 2023).
There has been a growing interest in AI research compared with earlier periods. Some studies have focused on the practical applications of AI, such as integrating AI tools into MA systems to improve the accuracy and efficiency of accounting information management and decision-making support (Arnaboldi et al., 2022; X. Zhang, 2021). Research has also explored the factors influencing the acceptance of AI in MA (Vărzaru, 2022a). Furthermore, significant attention has been given to assessing ethics and identifying key ethical risks associated with AI, including issues related to security, privacy, accountability, accessibility, and the associated benefits and challenges (Bocean & Vărzaru, 2022; Vărzaru, 2022c; C. Zhang et al., 2023). The studies on blockchain highlighted its context and applications in accounting systems, emphasizing efficiency, productivity, and security benefits (Faccia & Petratos, 2021; Wang et al., 2024), its impact on supply chain efficiency (Sahoo et al., 2022), and inter-organisational management control procedures (Kostić & Sedej, 2022).
There has also been a significant increase in studies focusing on environmental sustainability and its integration into MA through digital technologies. For example, Vărzaru et al. (2023) studied the roles of digitized MA in driving organisational sustainability within the healthcare industry, emphasizing the need for accounting professionals to acquire IT skills. Abdelhalim et al. (2023) investigated the moderating role of digitally supported environmental management accounting (EMA) in the relationship between eco-efficiency and corporate sustainability performance. Varma et al. (2024) explored the interdependence between financial and MA in enhancing eco-controls for sustainability reporting. Additionally, Di Vaio et al. (2023) emphasized the importance of accounting and accountability in relation to the circular economy and waste management.
Some studies explored the theme of accounting education (Hu, 2022; Pratama, 2024), emphasizing the importance of improving professional skills by enhancing the accounting curriculum simulation internship course. This interactive approach to higher education in the accounting field offers various pedagogical benefits (Sidorova et al., 2023) as it prepares future professionals for industry demands. For example, the integration of big data content into accounting education (Aboagye-Otchere et al., 2021), such as practical disciplines that can provide the development of professional skills in coding, statistics, AI, business intelligence (BI), and data visualization (Rautiainen et al., 2024). Moreover, an investigation into the extent to which accounting and auditing textbooks meet the requirements of digital transformation revealed that while textbooks are a primary resource, they inadequately cover IT-related topics because they do not fully meet the demands of the industry’s transition to the digital age (Oleiwi, 2023). There were also studies that contributed by developing research on the applicability of digital technologies within MA in specific business sectors, such as the hospital and healthcare sector (Fahlevi et al., 2022), SME (Ciampi et al., 2021), energy (Wei & Yao, 2020), and water distribution (Chen et al., 2022).
4.1.2 Authors
The analysis of author productivity and impact in a specific field is considered one of the most important bibliometric performance analyses. Identifying the top authors making significant contributions is important because it can serve as a guide for other authors, and an opportunity for the recognition of scientific excellence (Osare & Keshvari, 2023). In this section, the unit of analysis used to identify top authors was the number of publications and citations – typically considered the most prominent measures. A combination of productivity and impact metrics can contribute to an advanced analysis of overall research performance; considering that the number of publications is a proxy for productivity, the number of citations is still considered a leading measure of scientific impact and influence (Donthu et al., 2021; Mukherjee et al., 2022).
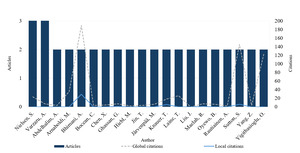
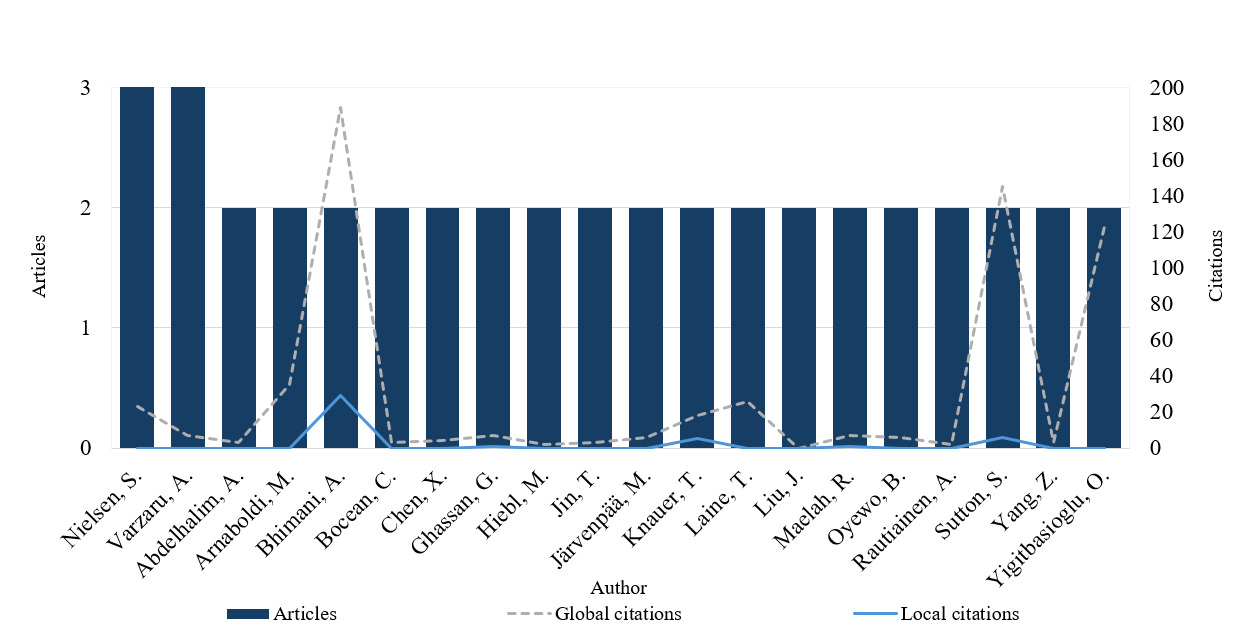
Considering this perspective, Figure 3 shows the top 20 most productive authors within the sample. This information was combined with the number of local and total citations, i.e., the number of each author’s citations in this bibliographic collection, and citations in other databases, respectively (Aria & Cuccurullo, 2017). According to this analysis, the authors most published were Steen Nielsen and Anca Antoaneta Vǎrzaru, focusing on business analytics and AI, respectively. Although these authors had published most, with three articles each, the more influential authors were Alnoor Bhimani and Leslie Willcocks, who co-authored a study on the impact of big data in accounting (Bhimani & Willcocks, 2014b). Although Figure 3 highlights the 20 most productive authors based on the number of publications, an additional analysis of total citation counts revealed other influential authors, such as Donald Warren, Kevin Moffitt, and Paul Byrnes, who co-authored an article with a similar focus on big data and its effects on accounting (Warren et al., 2015b).
In relation to productivity, the leading author was Steen Nielsen, who contributed three articles published between 2018 and 2023, with a focus on the applicability of business analytics in MA. The most influential paper was Reflections on the applicability of business analytics for management accounting – and future perspectives for the accountant (Nielsen, 2018). In this study, Nielsen (2018) explored the influence of business analytics in MA, highlighting its opportunities, implications for decision-making, and the necessary changes professionals must undergo regarding the use of these tools. According to (Nielsen, 2018), to add value in the business analytics environment, management accountants must increase not only their IT skills but also their statistical and econometric skills. Additionally, to enhance their analytical levels to apply a prescriptive approach, it is essential for professionals to focus on a holistic view of analytics culture, considering fact-based decisions that create value and impact, predictions and forecasts, and a visualized reporting process. In another article, Steen Nielsen highlighted the necessity of including exploratory data analysis and unsupervised ML in the field of MA, suggesting that the potential competitive advantage is higher when professionals apply more sophisticated analytics competences (Nielsen, 2022). However, according to Nielsen (2022), there is a gap in empirical research, as almost all reviewed articles are conceptual and do not address concrete examples of using AI and ML within MA. Another study focused on the integration of the balanced scorecard with the time-driven ABC model in the business analytics environment (Nielsen, 2023).
The second most productive author was Anca Antoaneta Vǎrzaru, with three articles published between 2022–2023. Her most influential paper was Assessing artificial intelligence technology acceptance in managerial accounting (Vărzaru, 2022a). According to Vărzaru (2022a), the most critical obstacles that interfere with adopting AI technology in MA are resistance to change, organisational culture, lack of trust, and the cost of technology. In this article, under behavioural theory approach, as empirical results Vărzaru (2022a) found a favourable attitude and a high intention to use AI in MA when the perceived advantages (innovation, rapidity, customization) outweighed the perceived disadvantages, including the need for high IT skills, potential job displacement in MA, and high implementation costs. In addition, her results also suggested that satisfaction among MA specialists positively impacts future use and behavioural intentions to use these technologies on a large scale. The focus of Anca Antoaneta Vǎrzaru’s investigations is AI, from different perspectives: cost; sustainability; and ethical issues, respectively, in Assessing digital transformation of cost accounting tools in healthcare (Vărzaru, 2022b), Assessing the contribution of managerial accounting in sustainable organisational development in the healthcare industry (Vărzaru et al., 2023) and Assessing the impact of AI solutions’ ethical issues on performance in managerial accounting (Vărzaru, 2022c). In this article, her aim was to investigate these ethical issues regarding the perception of accountants of the usefulness, efficiency, and effectiveness of implementing AI in MA. According to Vărzaru (2022c), the empirical results suggested the ethical issues of autonomy, responsibility, and trust significantly influenced the perceived usefulness and the performance of AI solutions. Her research concludes that although AI will substantially impact MA in the next few years, there are still many barriers and reluctance on the part of the accountants in relation to its use.
4.1.3 Journals
A journal is a leading path to disseminating knowledge as it serves as a representation of the authors who have published, and it can be considered as an indicator of the literature development of a particular research field (Aria et al., 2020). Furthermore, through the relevance of journals, it is possible to filter high-quality papers. Assessing the quality of scientific journals is becoming increasing important within the context of research performance evaluation (Mingers & Yang, 2017), considering the growing volume of scientific publications, because it helps to identify the most influential journals and understand where the most relevant research is being published. In this sense, this type of analysis can help researchers determine the most suitable journals for publishing their outputs. It also helps to identify trends and the classification of scientific research level of disciplines (Z. Zeng & Shi, 2021), allowing them to understand how research topics have been developed, and which areas have been actively investigated.
Table 1 presents the top 20 journals that published the most articles on MA and digital technologies within the scope of this sample, including their impact factor according to the Scimago and the Clarivate metrics. Moreover, to broaden the spectrum of analysis in relation to other journal evaluations, the table also provides the respective Academic Journal Guide (AJG) ranking assessment, a specific journal measurement for business and management-related fields.
The analysis revealed that the 140 articles were published in 100 different scientific journals. This variety of journals indicates the multidisciplinary perspectives and discussions related to MA and digital technologies. Despite these journals being multidisciplinary, most of the articles analysed were published in journals in the accounting, management, and business knowledge areas, followed by journals specializing in information systems and computational-related fields. Other knowledge areas have also published some articles, e.g. health, economics, and mathematics.
The International Journal of Accounting Information Systems and the Journal of Accounting and Organisational Change published the most articles, with seven in both journals. These journals are considered relevant in the accounting field, regarding issues associated with the integration of accounting and IT. The most covered topics related to the impact of business intelligence in management accounting practice, followed by the changed role of the accountant and the requirements for increasing their competency levels due to digital technologies’ advances. In addition, issues relating to the ethical impact of AI in managerial accounting were covered.
Next, Computational Intelligence and Neuroscience published five articles. This journal publishes research in the field of intelligent systems for computational neuroscience, including areas such as AI and computational theories. The most covered topics in these five articles discussed the role of artificial intelligence, big data, and data mining technology in the transformation of financial accounting to management accounting. Furthermore, the articles published in the Journal of Management Control (4), the European Accounting Review (3), and the Journal of Information Systems (3) encompassed subjects related to management accountants’ skills, organisational implications regarding the advancements function and digital technologies applied to the decision-making and management control processes.
4.1.4 Countries
Advances in digital technologies have significantly impacted MA practices and research globally. Understanding the development and specialisation of research in different contexts can help identify gaps and trends, contributing to research advancement. Considering research impact leads to structural change, benefiting many actors. This kind of analysis can also assist policymakers in identifying strategic research fields for their country and applying resources in these areas (Abramo et al., 2022).
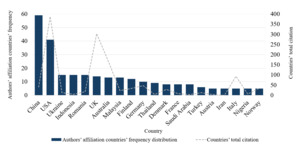
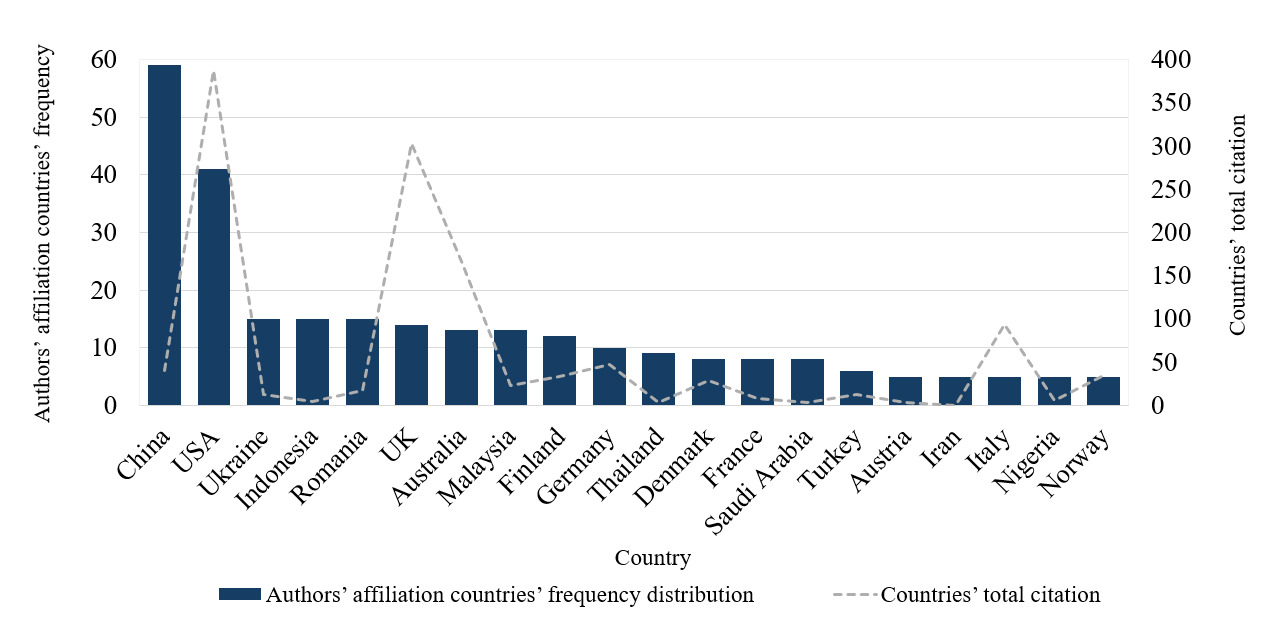
A country’s research performance is usually measured using variables such as the number of publications and citations. Here, the productivity and scientific impact of the countries were analysed, respectively, based on the authors’ affiliation countries’ frequency distribution (of all co-authors for each document) and the number of citations per document/country (Aria & Cuccurullo, 2017). Following this approach, Figure 4 presents each country’s research outputs from the sample under analysis. The analysis shows that authors are affiliated with institutions from 46 different countries. From the perspective of country frequency, the research outputs of the top 20 countries presented in the chart considered together corresponds to 80% of the sample. The top 10 most productive countries are China (17%), the USA (12%), Ukraine (5%), Indonesia (4%), Romania (4%), United Kingdom (4%), Australia (3%), Malaysia (4%), Finland (4%), and Germany (4%).
Considering productivity versus impact perspectives, China and the USA lead in published articles but differ in total citation counts, with the USA producing higher-impact studies. Articles with at least one author affiliated with an institution in China are relatively more recent, with a lower number of citations, and with various studies emphasizing discussions related to AI. These academic discussions include themes such as AI integration in MA information systems (Jia et al., 2022; Liu et al., 2022; Ping, 2021), the ethical impact of AI (C. Zhang et al., 2023), MA systems based on blockchain technology (Wang et al., 2024), the impact of BI in MA development (Bao et al., 2023), the internet of things (IoT) in the construction of MA information systems (Zhu & Liu, 2023), and cloud computing (Jin et al., 2022; X. Zhang, 2023).
Articles with at least one author affiliated with an institution in the USA tend to have a higher number of total citations. Additionally, recurrent themes include the impact of big data in MA (Warren et al., 2015), BI (Appelbaum et al., 2017; Elbashir et al., 2011; Peters et al., 2018), the impact of BI&A in MA (Appelbaum et al., 2017), and AI (Baldwin-Morgan, 1995; Dogru et al., 2023). Although Figure 4 only displays the top 20 countries based on authors’ affiliations, an additional analysis of total citation counts reveals that the top five most cited countries are the USA, UK, Australia, Iceland, and Canada. Together these five most cited countries account for approximately 72% of total citations in this sample, highlighting their influence on scientific knowledge production related to MA and digital technologies within this dataset. In studies conducted in the USA, the most cited articles focused on the impact of big data (Warren et al., 2015), and BI&A (Appelbaum et al., 2017; Elbashir et al., 2011). In contrast, of UK studies, the most cited articles were related to digitisation and big data in accounting (Bhimani & Willcocks, 2014), as well as innovative approaches within the SME context to enhance predictive outcomes (Ciampi et al., 2021). In the Australian context, the most cited papers focused on the use of BI&A in MA research (Rikhardsson & Yigitbasioglu, 2018), and the strategic integration of BI&A into MCS (Elbashir et al., 2011). Moreover, authors in Italy discussed digital transformation in relation to circularity and sustainability (Di Vaio et al., 2023), and SMEs (Ciampi et al., 2021).
This geographical analysis aligns with the findings of Sahoo et al. (2022) and Nguyen et al. (2023), emphasizing the necessity for more studies on MA and digital technologies in developing countries, along with their various technological application possibilities to gain a deeper understanding of the status of MA and digital technology research.
Summary of RQ1 Results
This section addressed RQ1 through a bibliometric analysis of 140 articles that focused on MA and digital technologies, offering an overview of this bibliographic sample, including publication years, authors, journals, and countries. In summary, this analysis showed that scientific production has grown in recent years, with 75% of articles published in the last five years, mainly due to advances in digital technologies (Steens et al., 2024), the increasing need for real-time information for decision-making (Appelbaum et al., 2017), regulatory changes (Nielsen, 2022), and interests in sustainability and social responsibility issues (Di Vaio et al., 2023). The most productive authors are Steen Nielsen and Anca Antoaneta Vǎrzaru, who focus on business analytics and AI, respectively. The most influential journals in this sample include the International Journal of Accounting Information Systems and the Journal of Accounting and Organisational Change. Both the USA and China are leaders in publication output, with the USA producing studies of high impact.
4.2 Science Mapping (RQ2)
4.2.1 Term Co-occurrence Analysis (RQ2)
The conceptual structure of the 140 studies was analysed using the VOSviewer’s text-mining functionality. This creates term maps based on a collection of documents to visually represent the field’s structure (N. J. van Eck et al., 2010). By analysing the titles and abstracts, the technique visualised the primary research areas based on the relatedness and co-occurrence of relevant terms. For this purpose, a binary counting method and a minimum of one occurrence of a term in the title and abstracts were the parameters to create the network visualisation map. Considering this, 3,846 terms were initially selected, resulting in a sample of 396 most relevant terms after a cleaning process. Within this sample and according to the software’s parameters, the 396 terms related to studies on MA and digital technologies were grouped into four distinct clusters.
These clusters were named by the authors based on the key ideas suggested by the relevant terms and their interactions within each cluster and the associated articles from which each term was extracted. The clusters are Cluster 1 (Artificial Intelligence and Blockchain), Cluster 2 (Information Technology and Cloud Computing), Cluster 3 (Big Data), and Cluster 4 (Business Intelligence).
Table 2 was created manually using the clustering process results from VOSviewer, following a similar classification proposal by Markoulli et al. (2017). It summarizes the main terms in each cluster coded into seven categories: the “technology terms” (i.e. the most relevant technology-related terms, e.g. “blockchain”), “process/action terms” (i.e. processes/actions terms related to MA or digital technologies, e.g. “cost management”), “theory terms” (i.e. theoretical approaches, e.g. “hierarchies’ theory”), “what terms” (i.e. concepts, e.g. “cost”), “who terms” (i.e. individual or collective actors, e.g. “accountant”), “where terms” (i.e. industries, work contexts, geographical areas, e.g. “banking”, “Malaysia”), and “how terms” (i.e. research design, statistical techniques, e.g. “quantitative research design”, “logistic regression”).
Cluster 1 – Artificial Intelligence and Blockchain. The first cluster comprises 119 terms. Based on the weight occurrences and total link strength of the terms’ relations, the analysis revealed that the most relevant terms related to digital technology are “artificial intelligence” and “blockchain”, which will be the focus of this subsection given that these technologies have gained increasing prominence in MA research. Other terms associated with digital technologies are “accounting information systems,” “ERP”, and “XBRL”. However, these last three terms are less significant in terms of their occurrence and link strength compared with the first two in the context of this analysis.
VOSviewer’s clustering algorithm identifies patterns of interconnection based on the semantic proximity and frequency of term co-occurrence within a search field (N. van Eck & Waltman, 2011). In this sense, the presence of AI and blockchain in this same cluster indicates a strong correlation between terms in the articles addressing these technologies within this bibliographic sample regarding MA and digital technologies, where these technologies are studied to improve accounting practices and related fields such as MA practices to support accurate decision-making (Nguyen et al., 2023; Vărzaru, 2022a), financial management (Y. Zeng, 2022), and audit (Al-Zaqeba et al., 2022; Kostić & Sedej, 2022). While debates about AI have discussed its benefits, for example, for predictive analysis, ML and automation of accounting processes (Shchyrba et al., 2024), discussions related to blockchain stand out for its ability to ensure transparency, traceability and security in financial transactions (Nguyen et al., 2023).
Artificial Intelligence. Articles associated with the term “artificial intelligence” addressed various perspectives, including the acceptance of AI solutions into MA systems (Vărzaru, 2022a). According to Vărzaru (2022a), the perceived benefits include efficiency and quality in the reporting processes and in decision-making. Debates also emphasized the importance of prioritizing technological advancement investments in AI applications to create value, improve operating performance, and increase revenue (Ranta et al., 2023), through their potential to accurately measure corporate performance, including revenue forecasting, cost analysis, predictive and prescriptive analysis (C. Zhang et al., 2023). In addition, they highlighted the importance of integrating sustainability into MA practices in promoting sustainable organisational development in the context of digital transformation (Vărzaru et al., 2023).
Despite the benefits of integrating AI into MA systems, some barriers to its acceptance include resistance to change, organisational culture, and lack of trust systems (Vărzaru, 2022a). Additionally, digital transformation requires changing the roles of the management accountants and controllers, including new identities and the need to develop new knowledge and skills – considered as one of the most challenging issues imposed by the technological advances (Rautiainen et al., 2024). In this context, discussions explored controllers’ perceptions regarding the necessary growth competencies and factors affecting the application of digital technologies (Steens et al., 2024), and the quality of accounting knowledge to provide important information for decision-making (Pratama, 2024), including the need for improving predictive data analysis and better performance measurement (Appelbaum et al., 2017).
AI can provide a comprehensive MA information system with holistic support, integrating independent and interconnected subsystems such as accounting analysis, risk management, performance management, and decision support (X. Zhang, 2021). Although there is a growing demand to enhance the intelligence of MA systems, the literature highlighted several challenges that hinder this process, including the difficulty of their AI integration. Some organisations have legacy systems that may not be compatible with modern AI technologies, which can be complex and expensive (Ciampi et al., 2021), limiting the flexibility and adaptability needed for their integration (X. Zhang, 2021). Moreover, issues related to interoperability (Bocean & Vărzaru, 2022) and technological infrastructure to support AI applications (Ping, 2021) are other challenges.
Debates also addressed data quality and availability (Vărzaru, 2022b), including the potential to explore unstructured and external data. According to Ranta et al. (2023), the ability to quantify qualitative and unstructured data to create new measures is a promising area that has not been fully explored. Existing systems focus on internal data, often neglecting external information, which can enhance the effectiveness of financial decision-making (Jia et al., 2022). Also, according to Arnaboldi et al. (2022), although AI is often seen as a tool for better decision-making, there are challenges in balancing algorithmic decision-making with human intuition. Both forms of decision-making have their strengths and weaknesses, such as biases and lack of transparency, which need to be addressed to avoid relying solely on one type (Arnaboldi et al., 2022). Furthermore, there are ethical concerns involving the impact of AI solutions, including transparency, security and autonomy (Vărzaru, 2022c; C. Zhang et al., 2023).
Although the integration of AI into MA systems is relevant, it remains at an early stage, leading to uncertainties about its full impact and potential benefits (Qiu, 2022; Vărzaru, 2022a). Furthermore, its application in accounting and MA is mainly theoretical, lacking concrete examples of how AI can be applied to MA (Nielsen, 2022). In this sense, some future research opportunities can be highlighted, such as more in-depth studies to understand how AI can be effectively utilised in MA (Qiu, 2022; Vărzaru, 2022a), integrated into existing MA systems (Ping, 2021) and its full impact in MA practices and decision-making processes (Vărzaru, 2022c). Research on frameworks and strategies is also needed for AI implementations that align capabilities with business goals, such as using balanced scorecards to measure performance (X. Zhang, 2021). In addition, there is a need for qualitative research focusing on a deeper analysis of how AI affects organisational transformations (Arnaboldi et al., 2022) and more comprehensive and systematic approaches applied to risk management (Y. Zeng, 2022). Moreover, future studies are needed to explore how to adapt MA methods to leverage AI’s capabilities effectively, ethical concerns (Vărzaru, 2022c) and how AI can be applied to improve data quality information and decision efficiency in sustainability contexts, especially in developing countries (Vărzaru et al., 2023).
Blockchain. Studies associated with the term “blockchain” addressed different perspectives, for instance, its integration in accounting and MA systems (Faccia & Petratos, 2021), automation of MA electronic transactions (Zadorozhnyi et al., 2018), its effect on sustainable performance when integrated into MA system (Nguyen et al., 2023), supply chain efficiency (Al-Zaqeba et al., 2022), and inter-organisational relationships (Kostić & Sedej, 2022). The integration of blockchain technology in MA offers the potential to make register processes more transparent, and efficient, allowing standardized, verifiable, and codifiable transactions (Kostić & Sedej, 2022), ensuring control and accountability (Al-Zaqeba et al., 2022), and allow the transfer of assets in a secure, private, and more cost-effective way (Shkulipa, 2021).
Additionally, beyond increasing the efficiency and effectiveness of data collection processes, blockchain’s decentralised and immutable ledger ensures that transactions recorded cannot be altered or deleted (Al-Zaqeba et al., 2022). Moreover, its traceability feature ensures that all recorded transactions can be traced back to their origin (Albaroodi & Anbar, 2022), which increases trust among stakeholders (Shkulipa, 2021), reduces risks of fraud and errors, and facilitates auditability and compliance (Wang et al., 2024).
Furthermore, the automation of MA transactions allows an increase in internal and external control over the execution of money operations due to timely and remote information sharing (Zadorozhnyi et al., 2018). Considering that information security and privacy are significant challenges for enterprises and management accountants (Shkulipa, 2021), a possible solution to these issues is integrating blockchain applications within information systems (Faccia & Petratos, 2021). However, this integration involves understanding and managing its technical complexities and can be costly, requiring substantial changes to ensure compatibility between blockchain solutions and their existing software and process (Kostić & Sedej, 2022; Nguyen et al., 2023). At the same time, while blockchain offers transparency, it can raise privacy concerns in relation to sensitive financial information that may be exposed to a public ledger, which could conflict with regulations that protect personal information (Albaroodi & Anbar, 2022). Regulatory issues, lack of standardisation, scalability challenges, cultural and organisational resistance to change, and skill gaps (Nguyen et al., 2023; Shkulipa, 2021; Wang et al., 2024) are other barriers that must be addressed to facilitate its successful application in MA routines.
Considering the emerging nature of blockchain technology and its potential applications in various fields, there is a need to focus on theoretical development, contextual analysis, and deployment strategies, especially in the areas of business management and decision-making (Sahoo et al., 2022). Furthermore, there is a need to explore blockchain technologies in the academic, professional organisations, and universities (Oleiwi, 2023), to develop professionals’ skills and understand the organisational competencies required for the effective integration of blockchain technology in MA systems and daily practices (Sahoo et al., 2022). Also, the literature has identified that blockchain studies have been conducted within supply chains mostly in developed countries (Al-Zaqeba et al., 2022; Faccia & Petratos, 2021), opening a call for studies within developing economies. Other gaps identified in the literature include a lack of empirical data supporting the theoretical benefits of blockchain integration in ERP and AIS systems (Faccia & Petratos, 2021), sustainability and ethical considerations (Sahoo et al., 2022), frameworks to address regulatory and compliance challenges (Wang et al., 2024), and the impact on accounting roles and accountant skills (Al-Zaqeba et al., 2022).
Regarding terms related to theories, the articles in this cluster addressed dynamic capability (Munir et al., 2023), institutional theory (Samanthi & Gooneratne, 2023), and managerial accounting theory (Berisha & Asllanaj, 2017). Using a framework that combines the theories of dynamic capability and socio-materiality, Munir et al. (2023) concluded that process-oriented dynamic capabilities, organisational culture, and the role of management accountants are strategically important for fostering innovation and achieving a competitive advantage in the era of artificial intelligence. According to institutional theory, Samanthi and Gooneratne (2023) found that the evolving roles of accountants are influenced by various rationalities based on their professional training, experience, organisational culture, global trends, and technological advancements.
Cluster 2 – Information Technology and Cloud Computing. The second cluster consists of 114 items, which the most relevant terms related to digital technology are “information technology” and “cloud computing”. The key terms in this cluster are linked to articles that discuss topics related to the integration of IT in MA systems, emphasizing its role in enhancing information accuracy, and improved decision-making for managers and investors (Najafi et al., 2022), challenges within innovations in IT, including data security and privacy concerns (Arnold, 2018), the importance of information quality (Kielanowicz et al., 2023), and information systems quality (Papiorek & Hiebl, 2023), the role of cloud computing in enabling cost efficiency, scalability, and real-time financial analytics (Al Lami et al., 2019).
Information Technology. IT allows more accessible and efficient work and increases the company’s performance due to rapid access to information and its processing (Svobodova, 2016). Its use impacts the quality of accounting information, influencing factors within the accounting system (Najafi et al., 2022), which is a basis for support in creating high-quality information used in the decision-making process (Kielanowicz et al., 2023). The use of IT in accounting routines, including cloud computing, improves competitiveness and lowers costs associated with technology adoption as accounting has been transforming into internet-based accounting (Al Lami et al., 2019).
Despite the benefits, IT systems can face significant security challenges that can lead to issues like fraud, manipulation, increased risk of financial misreporting (Najafi et al., 2022), and risk of data breaches – especially in fragmented systems that can compromise the integrity and confidentiality of MA data (Knauer et al., 2020). To overcome issues, organisations must protect sensitive MA data from unauthorised access (Arnold, 2018), ensuring data protection and implementing effective encryption and backup strategies (Guo, 2022). In addition, organisations may face challenges in adapting to rapid technological changes and ensuring that their IT systems remain up to date and aligned with evolving business needs (Papiorek & Hiebl, 2023).
Within studies related to IT, some future research areas were suggested, such as developing more quantitative studies to better understand the influence of digitalized information systems on the effectiveness of management control systems (Papiorek & Hiebl, 2023). Another area to explore is more robust security measures for IT systems to mitigate risks and improve reliability and security (Najafi et al., 2022), and investigate the potential use of unstructured data in MA, including social media, focusing on data reliability and integration into existing information systems (Knauer et al., 2020).
Cloud Computing. Cloud computing facilitates network access to a shared pool of configurable computing resources (Qin & Qin, 2021). Its application enhances MA in several ways, including resource sharing and real-time data exchange for informed decision-making (Al Lami et al., 2019), scalability and flexibility (Qin & Qin, 2021), and cost efficiency and resource optimization (X. Zhang, 2023). The real-time access allows managers to make informed decisions quickly and share MA information across different departments and stakeholders, enhancing collaboration and leading to more effective decision-making within organisations (Al Lami et al., 2019; X. Zhang, 2023).
Cloud computing also helps eliminate the high costs linked to maintaining physical IT infrastructure (Qin & Qin, 2021). It facilitates the management of large volumes of data, which helps to improve the speed and quality of data analysis (Al Lami et al., 2019), and enables access to advanced technologies such as AI and ML, which can be used to enhance data analysis and forecasting in MA (X. Zhang, 2023). In addition, researchers have explored the potential benefits for SMEs in using cloud computing, emphasizing its qualities such as agility, assurance, accountability, financial considerations, security and privacy, performance, and usability in the technology adoption process among SMEs (Al Lami et al., 2019). Although cloud computing provides these advantages, challenges include security and privacy concerns, compliance and regulatory issues, internet connectivity dependence, service provider dependence, and integration with existing systems (Qin & Qin, 2021; X. Zhang, 2023).
Regarding theory in this cluster, several theories were identified: theories of hierarchies and the perpetual accounting lag (Foster & Ward, 1994), diffusion of innovation theory (Di Vaio et al., 2023), new institutional sociology (Fahlevi et al., 2022), and stakeholder theory (Dogru et al., 2023). Foster and Ward (1994) combined the theories of hierarchies and the perpetual accounting lag to analyse the resistance to adopting MA innovations in hierarchical organisations. They found that internal labour markets prioritize cooperation and stability, hindering innovation and leading to outdated systems that result in suboptimal decision-making. Using the diffusion of innovation theory, Di Vaio et al. (2023) proposed a framework to understand how digital transformation can promote the adoption of accounting models that support sustainable development goals. Fahlevi et al. (2022) examined how technological innovations influenced management practices in hospitals using new institutional sociology, highlighting the role of new institutional routines and the benefits of technology adoption in enhancing cost efficiency in hospital operations. Dogru et al. (2023) combined stakeholder theory with the resource-based view to explore how digital innovation can be strategically employed to create value for various stakeholders while considering internal resources.
Future research could explore how to integrate more advanced analytics and ML into cloud systems to enhance insights into financial data, including forecasting (X. Zhang, 2023). Moreover, new studies could investigate how organisational culture influences the adoption of cloud technologies in MA and how emerging technologies impact the usefulness of cloud computing in MA (Al Lami et al., 2019).
Cluster 3 – Big Data. Cluster 3 contains 86 terms, with the most relevant terms being associated with big data. Articles associated with this term addressed topics such as the impact of big data on accounting and MA (Bhimani & Willcocks, 2014; Richins et al., 2017; Warren et al., 2015), the role of big data in strategic MA (Abdullah et al., 2022), big data analytics capabilities (Munir et al., 2023), decision quality (Franke & Hiebl, 2023), data mining (X. Zhang, 2021), and data management (Guo, 2022).
Big data refers to a complex collection of data that traditional data processing systems cannot effectively manage (Abdelhalim, 2023). It involves capturing, managing, processing and reporting data in real time for MA analysis (Franke & Hiebl, 2023). The integration of big data with MA practices provides timely information (Warren et al., 2015), leading to the elimination of repetitive tasks, allowing management accountants to focus more on evaluation, analysis, and interpretation (Franke & Hiebl, 2023). Furthermore, it enables real-time registration and integration of both internally and externally generated data (Rikhardsson & Yigitbasioglu, 2018).
Digitalisation offers opportunities for accountants to create value in innovative ways, helping to provide useful information in real time (Richins et al., 2017; Warren et al., 2015), providing predictive insights (Franke & Hiebl, 2023), and increased competitive advantage (Oyewo & Tran, 2021). Accountants must increase their technological, statistical and econometric skills (Nielsen, 2018) and develop analytical capabilities and take advantage of the technological opportunities (Franke & Hiebl, 2023). To make quality decisions, it is essential to have quality data and data analytics skills (Franke & Hiebl, 2023). While high-quality data allows management accountants to reliably perform their functions, such as planning, managerial control, and decision support (Knauer et al., 2020), poor-quality data of any type and from any source can negatively impact the management accountant’s work, rendering forecasts to be incorrect (Appelbaum et al., 2017), causing them to make the wrong decisions and potentially compromising the performance and even the existence of the company.
The literature emphasized management accountants’ practices, new competencies and necessary skills (Franke & Hiebl, 2023), for improving predictive data analysis, better performance measurement (Appelbaum et al., 2017), and the benefit from these technologies in decision-making (Oesterreich & Teuteberg, 2019; Steens et al., 2024). Moreover, it highlighted the role of the accounting profession, the requirements for technological implementation, and the need for adaptations in accounting practices (Järvenpää et al., 2023; Steens et al., 2024).
Regarding theories, contingency theory (Rasit & Ismail, 2017), competency theory (Steens et al., 2024), sensemaking theory (Järvenpää et al., 2023), and organizational information processing theory (Szukits, 2022) were the key theories identified in this cluster. Using competence theory, Steens et al. (2024) investigated how advancing digital technologies impact controllers’ competency requirements. Their findings indicate that senior controllers perceive their current technological skills as insufficient and may also underestimate the digital competencies necessary to remain relevant in the future. Järvenpää et al. (2023) also studied controllers but through sense-making theory perspective and found that management accountants are sense-givers as they filter and interpret data, fostering shared understanding and trust in the information used for decision-making. Additionally, organizational information processing theory was applied by Szukits (2022) to analyse the impact of advanced analytics in businesses and found that a firm’s commitment to digital technologies is necessary for effective leveraging of advanced analytics in the decision-making process and highlighted the key role of controllers in interpreting and integrating analytical insights.
Further empirical research could explore the relevance of controllers’ digital competencies, including understanding how these competencies impact their roles, ensuring they are prepared to face the demands of advancing technologies (Steens et al., 2024). It includes understanding programming principles and emerging technologies. Future research could investigate the best methods for integrating these skills into accounting education and professional development to ensure they remain relevant in a data-driven world (Richins et al., 2017). In addition, it could examine the development and implementation of more advanced data-mining techniques and algorithms tools to improve accuracy and efficiency in decision-making in financial contexts (Ionescu, 2022) and the integration of big data analytics into accounting education, including curriculum design and pedagogy to prepare students for the evolving demands of the industry (Aboagye-Otchere et al., 2021). Furthermore, MA researchers need to reevaluate traditional methodological principles when studying contexts involving digital data. According to Bhimani (2020), investigating big data in MA requires researchers to consider multidisciplinary approaches and innovative research methods, such as mixed methods and a grounded theory perspective to address research questions that have not been previously explored.
Cluster 4 – Business Intelligence. The fourth cluster comprises 77 items, among which the most relevant term is “business intelligence” (BI). This term is linked to articles that addressed, for instance, the impact of business intelligence and business analytics on MA (Appelbaum et al., 2017; Rikhardsson & Yigitbasioglu, 2018), the applicability of business analytics for MA (Nielsen, 2018, 2023), the role of business analytics in the management accountant’s competence (Järvenpää et al., 2023; Oesterreich & Teuteberg, 2019), and critical success factors for the implementation of business intelligence in MA (Mauludina et al., 2023).
BI involves a set of tools, processes, and technologies that transform raw data into insights to optimise decision-making processes (Kalantari et al., 2012). Different from other systems, such as executive information system and decision support system, BI broadly refers to management support system designed for informed and strategic decision-making (Peters et al., 2018), providing a more comprehensive approach to performance measurement, and increased efficiency and accuracy (Appelbaum et al., 2017). Moreover, it allows real-time data utilization, improved forecasting and budgeting, increased cognitive load, lead decentralisation in MA tasks, and skill evolution (Rikhardsson & Yigitbasioglu, 2018). It also provides informed decision-making in uncertainty and for risk mitigation strategies, and predictive and prescriptive analysis (Nielsen, 2023). This technology altered the expected competencies profile of management accountants, requiring business analytics skills, including knowledge of quantitative and statistical methods, data acquisition, preparation, integration, analysis and visualisation (Oesterreich & Teuteberg, 2019). In addition, it has impacted the role of the accounting profession, the requirements for technological implementation, and the need for adaptations in accounting practices (Järvenpää et al., 2023; Steens et al., 2024). According to Mauludina et al. (2023), the critical success factors of BI implementation include user capabilities, organisational collaboration, effective data management and governance, committed management support and sponsorship, a business-driven and scalable technical framework, and sustainable data quality and integrity.
Regarding theory, this analysis identified absorptive capacity theory (Elbashir et al., 2011), organisational theory (Lhuillery et al., 2023), and fuzzy theory (Bian & Bian, 2022). Elbashir et al. (2011) applied the absorptive capacity theory and found that organisational absorptive capacity is crucial for the successful integration of BI systems into MCS and highlighted the role of dynamic knowledge, cultural controls, and the top manager in leveraging new technologies for organisational benefit at both strategic and operational levels. Lhuillery et al. (2023) addressed absorptive capacity theory and organisational theory in the audit department context and highlighted factors that promote audit innovations, such as digital technologies and horizontal internal learning over vertical learning, routines, and job rotation. Using fuzzy theory, Bian and Bian (2022) found that integrating network algorithms into the MA model allows for high efficiency and precision in processing complex text and data within MA, enhancing decision-making processes significantly.
Regarding empirical studies focused on implementing BI in MA, Mauludina et al. (2023) identified a gap in this field and suggested future research to investigate how BI can be integrated with AI and identified the success factors for such integration in real-world settings. Future research should also investigate the moderating relationships in BI systems to develop and test theories regarding BI functionalities and organisational improvisation (Peters et al., 2018). Furthermore, other suggestions for future studies include investigating task complexity and other job-related factors in influencing BI systems success in MA practices (Mudau et al., 2024) and how different decision types influence BI outcomes across various industries (Bao et al., 2023). It is also important to understand the impact of predictive analytics on MA practices. Thus, research could investigate how predictive analytics tools influence management control systems, decision-making processes and organisational efficiency (Fehrenbacher et al., 2023). Furthermore, there is a gap in understanding the specific skills and competencies required to thrive in the digital era. Future studies could focus on identifying these skills and developing training programs to equip accountants for future challenges and how regulatory changes and their effects will reshape the roles and responsibilities of management accountants (Rautiainen et al., 2024).
Summary of RQ2 Results
This section addressed RQ2 by applying the term co-occurrence analysis to understand the conceptual structure of studies on MA and digital technologies. The analysis revealed that studies in this field can be categorized into four clusters as detailed above.
This analysis showed how MA has been impacted due to digital transformation, with each cluster addressing a distinct but interconnected aspect of digital technology adoption. Cluster 1 highlighted discussions on the integration of emerging tools, AI and blockchain, into traditional accounting systems, shedding light on how efficiency and data security can be improved (Arnaboldi et al., 2022; Nguyen et al., 2023; Vărzaru, 2022a). However, several challenges hinder their acceptance in MA practices, such as difficulties in integration within current systems, lack of technological infrastructure, costs, resistance to change, lack of skills, and ethical concerns (Nielsen, 2022; Ping, 2021; Rautiainen et al., 2024). Within this cluster, some future research opportunities were highlighted. These include empirical studies on AI applications on MA systems (Nielsen, 2022; Qiu, 2022; Vărzaru, 2022a), frameworks and strategies for AI implementations (X. Zhang, 2021), MA methods to leverage AI’s capabilities effectively, and ethical concerns (Vărzaru, 2022c).
Cluster 2 addressed debates related to IT and cloud computing adoption within accounting and MA systems, focusing on their roles in enhancing information accuracy, and improved decision-making (Najafi et al., 2022), data security and privacy concerns (Arnold, 2018), the role of cloud computing in enabling cost efficiency, scalability, and real-time financial analytics (Al Lami et al., 2019). This analysis highlighted some future research opportunities, such as the integration of advanced analytics into cloud systems (X. Zhang, 2023), how organisational culture influences the adoption of cloud technologies in MA and how emerging technologies impact the usefulness of cloud computing in MA (Al Lami et al., 2019).
Cluster 3 focused on big data transforming MA practices and management accountant roles (Bhimani & Willcocks, 2014; Richins et al., 2017; Warren et al., 2015), big data in strategic MA (Abdullah et al., 2022), and big data analytics capabilities (Munir et al., 2023). Suggestions for future research include controllers’ digital competencies (Steens et al., 2024), advanced data mining techniques and algorithms tools to improve accuracy and efficiency in decision-making (Ionescu, 2022), the integration of big data analytics into accounting education, including curriculum design (Aboagye-Otchere et al., 2021), and new methodological principles for MA research in the context of big data (Bhimani, 2020).
Finally, Cluster 4 addressed business intelligence, automation, and evolving control systems, demonstrating how integrated analytics can guide both daily strategic tasks (Appelbaum et al., 2017; Nielsen, 2023; Ranta et al., 2023). Within this cluster, suggestions for future studies include empirical studies focused on implementing BI in MA (Mauludina et al., 2023), investigating task complexity (Mudau et al., 2024), decision types’ influence on BI outcomes (Bao et al., 2023), predictive analytics tools influencing decision-making processes and organisational efficiency (Fehrenbacher et al., 2023), and the skills required to thrive in the digital era (Rautiainen et al., 2024).
These clusters collectively highlighted the field of MA in ongoing transition, driven by technological innovation and characterized by discussions regarding advantages, challenges, theoretical foundations, practical implications, ethical considerations, and the competencies required for management accountants.
5. Concluding Comments
This study analysed 140 articles from Scopus and WoS to investigate the advances in research outputs related to MA and digital technologies. This analysis indicated that research approaches in this field have been developed in a multidisciplinary approach, covering theoretical and practical applications of digital tools and addressing issues such as security (Di Vaio et al., 2023), data quality (Knauer et al., 2020), the need for constant innovation (Munir et al., 2023), required skills (Steens et al., 2024), and ethical concerns (Vărzaru, 2022c). The most discussed technologies included blockchain (Kostić & Sedej, 2022; Nguyen et al., 2023), artificial intelligence (Nielsen, 2022; Vărzaru, 2022a), business intelligence and analytics tools (Järvenpää et al., 2023; Nielsen, 2023), and cloud computing (Ionescu, 2022; Jin et al., 2022).
The literature emphasized the strategic adoption of digital technologies in MA, highlighting benefits such as improved efficiency (Faccia & Petratos, 2021), the potential to accurately provide real-time insights for decision-making, including predictive and prescriptive data-driven analysis (Appelbaum et al., 2017). These benefits also provide improved analysis of both operational and financial performance, helping managers make better strategic, tactical, and operational decisions (Igulu et al., 2023), which may also improve transparency and security (Di Vaio et al., 2023).
Despite the potential benefits digital technology innovations may offer to MA practices and techniques, there are challenges to be addressed, such as security and data privacy concerns (Di Vaio et al., 2023; Wang et al., 2024), technical complexity, the cost of implementation, and cultural resistance (Kostić & Sedej, 2022; Nguyen et al., 2023). Moreover, the lack of digital competencies, including statistical and econometric skills, was pointed out as a barrier to the acceptance and adoption of digital technology by management accountants, hindering the ability of management accountants to fully leverage the benefits that these technologies can provide for a strategic decision-making process (Nielsen, 2018; Steens et al., 2024). Ethical concerns were also highlighted in digital technology implementation (Vărzaru, 2022c; C. Zhang et al., 2023), including privacy and accountability issues (Bocean & Vărzaru, 2022).
Regarding RQ1, the analysis showed that nearly 75% of the articles examined were published in the last five years. This can be attributed to technological advances, the need for real-time information, regulatory changes and accounting standards, the demand for efficiency and cost control (Appelbaum et al., 2017; Nielsen, 2022; Steens et al., 2024), as well as the growing interest in sustainability and social responsibility issues (Di Vaio et al., 2023). The International Journal of Accounting Information Systems and the Journal of Accounting and Organisational Change were the most influential journals in this sample, each having published seven articles. The most productive authors were Steen Nielsen and Anca Antoaneta Vǎrzaru, focusing on business analytics and AI, respectively. In terms of country affiliation, the USA and China are leaders in publication output, with the USA producing studies of high impact.
For RQ2, the term co-occurrence analysis revealed that the conceptual structure of this set of articles may be grouped into four main research streams: artificial intelligence and blockchain, information technology and cloud computing, big data, and business intelligence. This analysis showed how MA has been impacted due to digital transformation, with each cluster addressing a distinct but interconnected aspect of digital technology adoption, including benefits, challenges, theoretical foundations, practical implications, ethical considerations, and the competencies required for management accountants.
Based on the gaps identified in this analysis, some themes are suggested for future research. First, research should explore how AI and blockchain can enhance credit access for SMEs and streamline financial resource management for their managers. Second, there is a need to understand the potential of AI, blockchain, and advances in MA methods in contributing to social and environmental sustainability. In addition, educational institutions should consider adjusting accounting courses to prioritize statistical skills for big data analysis, equipping management accountants with the necessary tools to effectively utilize digital technologies, including AI and blockchain. Furthermore, more empirical studies are required to understand the relationship between MA and digital technologies, particularly AI. Finally, it is worth exploring how AI and blockchain-based digital technologies can be employed in the government sector to enhance financial reporting, improve managerial transparency, and promote social participation through initiatives like participatory budgeting and social control mechanisms.
This study’s limitations include using selected bibliographic databases for the sample, the search strategies, keywords used, bibliometric analysis, and the science mapping techniques applied. Future research conducting bibliometric analysis should consider using additional bibliographic databases to provide a broader analysis perspective, including articles not considered in this sample. Future works could also be developed by considering other bibliometric analysis techniques not included in this study. Techniques such as countries’ scientific production, most cited countries, or most relevant affiliations could provide new insights. For instance, they can help identify countries’ scientific productivity and impact, the most debated academic discussions about MA and digital technologies, and the most influential countries in this knowledge area. We also suggest future research to explore other perspectives in science mapping analysis techniques, such as co-authorship and co-citation analysis. These techniques can help map out the social and intellectual structures, respectively.
Acknowledgements
This study was conducted at the Research Center on Accounting and Taxation (CICF) and was funded by the Portuguese Foundation for Science and Technology (FCT) through national funds (PRT/BD/154685/2023, UIDB/04043:CICF, and UIDP/04043:CICF). The authors thank Polytechnic University of Cávado and Ave (IPCA), RUN-EU and the Technological University of the Shannon: Midlands Midwest (TUS). The authors also thank the anonymous reviewers for their valuable contributions, the editor Prof. Martin Quinn for his editorial guidance and insightful comments, and Prof. Mike Farrell for his constructive feedback.
Twitter, known as X since 2023, is referred to as “Twitter” here to maintain consistency with the terminology used in the original studies cited.
The analyzed metadata sample was retrieved from Scopus in April 2024.
The analyzed metadata sample was retrieved from WoS in April 2024.